管庄地区网站建设链接买卖价格
目录
一、链表的八种结构
二、带头双向循环链表的实现
1.链表的定义
2.链表的接口定义
3.接口的具体实现
三、带头双向循环链表的完整代码
四、顺序表和链表的区别
一、链表的八种结构
我们已经知道链表可以有以下三种分法
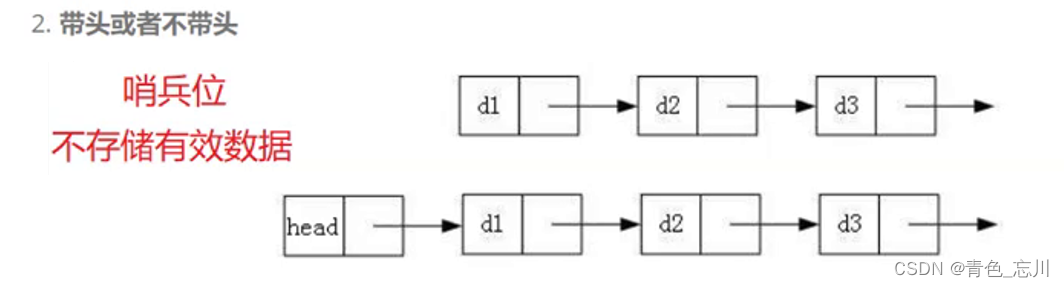
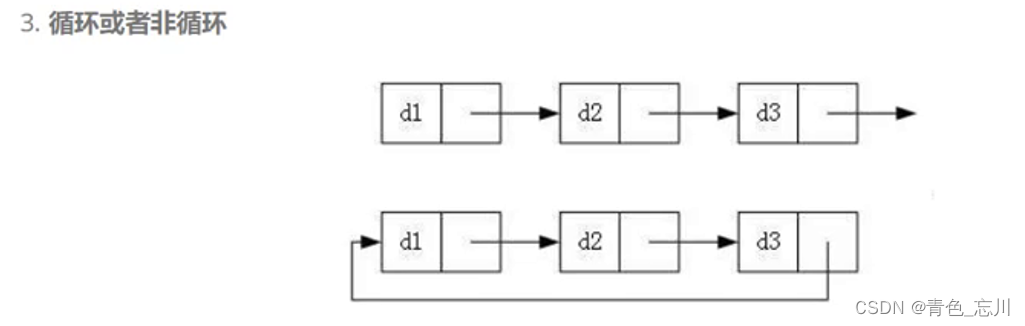
而这三种结构又可以排列组合,形成八种结构
其中我们最常见的就是无头单向非循环链表和带头双向循环链表
1.无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。
2. 带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。另外这个结构虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现结构会带来很多优势,实现反而简单了
二、带头双向循环链表的实现
1.链表的定义
对于这个链表,我们需要使用两个指针来控制,一个是前驱指针,一个是后继指针
typedef int LTDateType; typedef struct ListNode {struct ListNode* prev;struct ListNode* next;LTDateType data; }ListNode;
2.链表的接口定义
如下代码所示,是我们需要实现的接口
//链表的初始化 ListNode* ListCreat(); //链表的打印 void ListPrint(ListNode* phead); //链表的尾插 void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x); //链表的头插 void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x); //链表是否为空 bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead); //链表的尾删 void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead); //链表的头删 void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead); //链表的查找 ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x); //链表在pos前面的插入 void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDateType x); //链表在pos位置处的删除 void ListErase(ListNode* pos); //链表的销毁 void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead);
3.接口的具体实现
1.链表的初始化
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDateType x) {ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode; } //链表的初始化 ListNode* ListCreat() {ListNode* phead = BuyListNode(-1);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead; }如上代码所示,对于这个初始化,他与单链表不同,单链表其实是没有必要去专门做一个初始化函数的。但同时我们需要传二级指针来解决一些问题
对于双向带头循环链表,我们就有必要设置一个初始化函数了。
我们有两种思路去构建这个函数
一种是在主函数中直接定义一个指针,然后通过传这个指针的地址去构建。但是这样我们就需要传二级指针了。
另外一种是我们可以利用返回值,这样我们就直接避免了传参数了。
2.链表的打印
//链表的打印 void ListPrint(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;printf("<=head=>");while (cur != phead){printf("%d<=>", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n"); }如上代码所示,链表的打印与单链表的打印是一样的,没有什么太大的区别,我们可以利用printf来更加形象的表达双向循环的意思
3.链表的尾插
//链表的尾插 void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x) {assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);ListNode* tail = phead->prev;tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode; }对于尾插就比单链表简单多了,因为有了头节点,我们就不需要处理是否为空的状态了
4.链表的头插
//链表的头插 void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x) {assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);ListNode* first = phead->next;phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = first;first->prev = newnode; }头插和尾插基本上是非常类似的,这也得益于这种链表结构基本是无死角的
5.链表的头删尾删以及是否为空
//链表是否为空 bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);return phead->next == phead; } //链表的尾删 void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);assert(!ListEmpty(phead));ListNode* tail = phead->prev;ListNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;phead->prev = tailPrev;tailPrev->next = phead;free(tail);tail = NULL; } //链表的头删 void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);assert(!ListEmpty(phead));ListNode* first = phead->next;ListNode* firstNext = first->next;phead->next = firstNext;firstNext->prev = phead;free(first);first = NULL; }对于头删和尾删其实也是一致的思路,我们只需要改变结点即可,值得注意的是,我们需要判断链表是否为空, 如果为空肯定不可以删除
6.链表的查找
//链表的查找 ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead,LTDateType x) {assert(phead);assert(!ListEmpty(phead));ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL; }这个也是比较简单的,他的思路与单链表的是一样的
7.链表在pos位置之前插入
//链表在pos前面的插入 void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDateType x) {assert(pos);ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode; }这个的话,我们更能体会到他相对于单链表的优势了。我们只需要pos位置即可。然后思路和头插尾插是一致的
8.链表在pos位置的删除
//链表在pos位置处的删除 void ListErase(ListNode* pos) {assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);pos = NULL; }对于删除,也是与头删尾删思路一致的
9.链表的销毁
//链表的销毁 void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);phead = NULL; }对于链表的销毁思路与单链表也是一致的,只需要循环遍历即可
三、带头双向循环链表的完整代码
List.h
#pragma once #include<stdio.h> #include<malloc.h> #include<assert.h> #include<stdbool.h> typedef int LTDateType; typedef struct ListNode {struct ListNode* prev;struct ListNode* next;LTDateType data; }ListNode;//链表的初始化 ListNode* ListCreat(); //链表的打印 void ListPrint(ListNode* phead); //链表的尾插 void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x); //链表的头插 void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x); //链表是否为空 bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead); //链表的尾删 void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead); //链表的头删 void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead); //链表的查找 ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x); //链表在pos前面的插入 void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDateType x); //链表在pos位置处的删除 void ListErase(ListNode* pos); //链表的销毁 void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead);
List.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 #include"List.h" ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDateType x) {ListNode* newnode = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc");return NULL;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;newnode->prev = NULL;return newnode; } //链表的初始化 ListNode* ListCreat() {ListNode* phead = BuyListNode(-1);phead->next = phead;phead->prev = phead;return phead; } //链表的打印 void ListPrint(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;printf("<=head=>");while (cur != phead){printf("%d<=>", cur->data);cur = cur->next;}printf("\n"); } //链表的尾插 void ListPushBack(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x) {assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);ListNode* tail = phead->prev;tail->next = newnode;newnode->prev = tail;newnode->next = phead;phead->prev = newnode; } //链表的头插 void ListPushFront(ListNode* phead, LTDateType x) {assert(phead);ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);ListNode* first = phead->next;phead->next = newnode;newnode->prev = phead;newnode->next = first;first->prev = newnode; } //链表是否为空 bool ListEmpty(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);return phead->next == phead; } //链表的尾删 void ListPopBack(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);assert(!ListEmpty(phead));ListNode* tail = phead->prev;ListNode* tailPrev = tail->prev;phead->prev = tailPrev;tailPrev->next = phead;free(tail);tail = NULL; } //链表的头删 void ListPopFront(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);assert(!ListEmpty(phead));ListNode* first = phead->next;ListNode* firstNext = first->next;phead->next = firstNext;firstNext->prev = phead;free(first);first = NULL; } //链表的查找 ListNode* ListFind(ListNode* phead,LTDateType x) {assert(phead);assert(!ListEmpty(phead));ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){if (cur->data == x){return cur;}cur = cur->next;}return NULL; } //链表在pos前面的插入 void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDateType x) {assert(pos);ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;prev->next = newnode;newnode->prev = prev;newnode->next = pos;pos->prev = newnode; } //链表在pos位置处的删除 void ListErase(ListNode* pos) {assert(pos);ListNode* prev = pos->prev;ListNode* next = pos->next;prev->next = next;next->prev = prev;free(pos);pos = NULL; } //链表的销毁 void ListDestroy(ListNode* phead) {assert(phead);ListNode* cur = phead->next;while (cur != phead){ListNode* next = cur->next;free(cur);cur = next;}free(phead);phead = NULL; }
Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1#include"List.h"void TestList1() {ListNode* plist = ListCreat();ListPushBack(plist, 1);ListPushBack(plist, 2);ListPushBack(plist, 3);ListPushBack(plist, 4);ListPushBack(plist, 5);ListPrint(plist);ListPushFront(plist, 6);ListPushFront(plist, 7);ListPushFront(plist, 8);ListPushFront(plist, 9);ListPushFront(plist, 10);ListPrint(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPopBack(plist);ListPrint(plist);ListPopFront(plist);ListPopFront(plist);ListPopFront(plist);ListPopFront(plist);ListPrint(plist);} void TestList2() {ListNode* plist = ListCreat();ListPushBack(plist, 1);ListPushBack(plist, 2);ListPushBack(plist, 3);ListPushBack(plist, 4);ListPushBack(plist, 5);ListPrint(plist);ListNode* pos = ListFind(plist, 3);(pos->data) *= 10;ListPrint(plist);ListInsert(pos, 20);ListPrint(plist);ListErase(pos);ListPrint(plist);} int main() {//TestList1();TestList2();return 0; }
四、顺序表和链表的区别
不同点 顺序表 链表 存储空间上 物理上一定连续 逻辑上连续,但物理上不一定连续 随机访问 支持,O(1) 不支持,O(N) 任意位置插入或删除元素 可能需要搬移元素,效率低,O(N) 只需要改变指针指向 插入 动态顺序表,空间不够时需要扩容 没有容量的概念 应用场景 元素高效存储+频繁访问 任意位置插入和删除频繁 缓存利用率 高 低
如上表所示,是顺序表和链表的区别
在这里我们需要注意缓存利用率这个东西。
对于我们的顺序表/链表,想要实现他的数据访问、遍历、修改等
这些数据是由cpu来进行访问的。
也就是这些访问的指令都是cpu执行的。从而访问打印等操作。这时候cpu就需要去访问内存
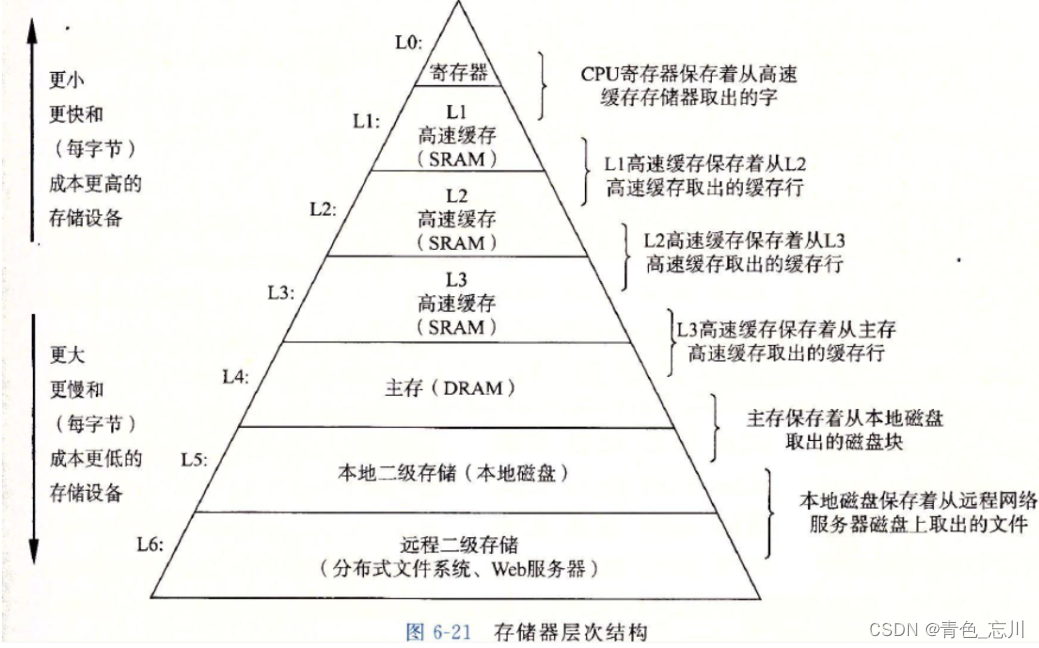
而cpu其实是不能直接访问内存的,这是因为cpu太快了,内存太慢了
为了解决这个问题,就有了三级缓存,即cpu高速缓存这个东西。
也就是说cpu会先访问缓存,最高级的缓存再次缓存其实就是命中。
在计算机中有一个局部性原理,在访问某个位置的数据的时候,大概率要访问后面的数据。因此他就会将这个数据后面的数据也顺便加载进去。
这时候由于顺序表是连续的,后面的都直接被命中了。所以他的缓存利用率高
而链表他访问某个数据的时候也会加载一长段,但是后面的不一定会用。所以就会浪费,也会导致缓存污染。所以缓存利用率低。也就是他不仅没有起到正向作用,反而起到了反向作用。
本节内容到此位置
如果对你有帮助的话,不要忘记点赞加收藏哦!!!