顺德网站建设代理商app地推接单平台有哪些
文章目录
- 说明
- day1 环境搭建
- 1.1 开发环境
- 1.2 package import 和 println
- 1.3 编写HelloWorld.java
- day2 基本算术操作
- 2.1 加、减、乘、除、整除、取余.
- day3 基本if 语句
- 3.1 if条件分支语句
- 3.2 代码
- day4 闰年的计算
- 4.1 思路整理:何为闰年?
- 4.2 核心代码
- day5 基本switch 语句
- 5.1 switch也属于条件分支语句
- 5.2 思考
- day6 基本for 语句
- 6.1 for语句中表达式的执行顺序
- 6.2 代码
- day7 矩阵元素相加
- 7.1 题目解读
- 7.2 二维数组中
- day8 矩阵相乘
- 8.1 题目解读
- 8.2代码
- day9 while 语句
- 代码
- day10 综合任务 1
- 10.1 题目解读
- 10.2 代码
- 自我小结
- 三大结构
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
day1 环境搭建
1.1 开发环境
在搭建java环境时,从官网下载了java安装包安装成功后,一定要正确配置环境变量
1.2 package import 和 println
(1)package包:就好似我们日常生活中的”收纳盒“,不同的”收纳盒“装不同的”物品“,方便我们查找和定位。在大”收纳盒“中有包含各种小”收纳盒“,这也体现了包是以树形结构存储的。
package com //一个主包
package com.project //主包下建一个项目工程包
package com.project.util //一个工具包,util工具包在com目录下的project目录中
(2)import:导入包成员,在写一个java类时,我们需用到其他包中的成员,此时就需要通过import导入相应的包,则就好似c语言需要导入头文件,才能用一些库里的函数
import java.util.ArrayList;; //导入Java util包下的ArrayList 那则可以用这个类中一些方法,变量
import java.util.*; //导入util包下所有的东西,那我们使用的范围就比上面这个更多
(3)println:打印输出语句,且在输出后会自动换行,若不换行则是print
1.3 编写HelloWorld.java
main函数是程序入口
package basic;
public class HellowWorld {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println("Hello, World");}
}
day2 基本算术操作
2.1 加、减、乘、除、整除、取余.
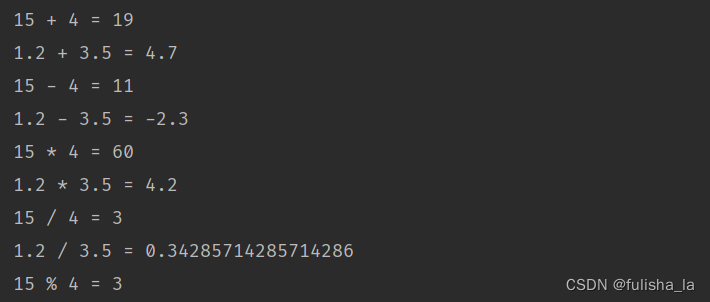
package basic;public class BasicOperations {public static void main(String args[]) {int tempFirstInt, tempSecondInt, tempResultInt;double tempFirstDouble, tempSecondDouble, tempResultDouble;tempFirstInt = 15;tempSecondInt = 4;tempFirstDouble = 1.2;tempSecondDouble = 3.5;//AdditiontempResultInt = tempFirstInt + tempSecondInt;tempResultDouble = tempFirstDouble + tempSecondDouble;System.out.println("" + tempFirstInt + " + " + tempSecondInt + " = " + tempResultInt);System.out.println("" + tempFirstDouble + " + " + tempSecondDouble + " = " + tempResultDouble);//SubtractiontempResultInt = tempFirstInt - tempSecondInt;tempResultDouble = tempFirstDouble - tempSecondDouble;System.out.println("" + tempFirstInt + " - " + tempSecondInt + " = " + tempResultInt);System.out.println("" + tempFirstDouble + " - " + tempSecondDouble + " = " + tempResultDouble);//MultiplicationtempResultInt = tempFirstInt * tempSecondInt;tempResultDouble = tempFirstDouble * tempSecondDouble;System.out.println("" + tempFirstInt + " * " + tempSecondInt + " = " + tempResultInt);System.out.println("" + tempFirstDouble + " * " + tempSecondDouble + " = " + tempResultDouble);//DivisiontempResultInt = tempFirstInt / tempSecondInt;tempResultDouble = tempFirstDouble / tempSecondDouble;System.out.println("" + tempFirstInt + " / " + tempSecondInt + " = " + tempResultInt);System.out.println("" + tempFirstDouble + " / " + tempSecondDouble + " = " + tempResultDouble);//ModulustempResultInt = tempFirstInt % tempSecondInt;System.out.println("" + tempFirstInt + " % " + tempSecondInt + " = " + tempResultInt);}
}
day3 基本if 语句
3.1 if条件分支语句
其中,if中的表达式应该为布尔表达式。这里会存在三种不同选择。(假设在if中会有数据的处理)
第一,只使用if语句,这相当于我只过滤我想要的数据;
第二:if…else 语句,(不入if就进else, 非真即假)
第三:if…else if…else 语句,这就是多条件分支判断。对不同条件进行判断
3.2 代码
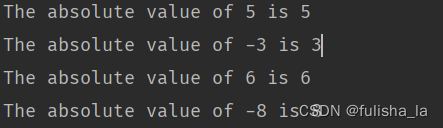
package basic;public class IfStatement {/*** The entrance of the program* @param args*/public static void main(String args[]) {int tempNumber1, tempNumber2;// Try a positive valuetempNumber1 = 5;if (tempNumber1 >= 0) {tempNumber2 = tempNumber1;} else {tempNumber2 = -tempNumber1;} // Of ifSystem.out.println("The absolute value of " + tempNumber1 + " is " + tempNumber2);// Try a negative value// Lines 27 through 33 are the same as Lines 15 through 19tempNumber1 = -3;if (tempNumber1 >= 0) {tempNumber2 = tempNumber1;} else {tempNumber2 = -tempNumber1;} // Of ifSystem.out.println("The absolute value of " + tempNumber1 + " is " + tempNumber2);// Now we use a method/function for this purpose.tempNumber1 = 6;System.out.println("The absolute value of " + tempNumber1 + " is " + abs(tempNumber1));tempNumber1 = -8;System.out.println("The absolute value of " + tempNumber1 + " is " + abs(tempNumber1));}/*** @param paraValue The given value.* @return The absolute value of the given parameter.*/public static int abs(int paraValue) {if (paraValue >= 0) {return paraValue;} else {return -paraValue;}}
}
day4 闰年的计算
4.1 思路整理:何为闰年?
(1)非世纪年(不能被100整除的年份)能被4整除且不能被100整除的年份为闰年
(2)世纪年 能被400整除的才是闰年
文中给出两种计算闰年的方法,结合day3的if语句,第一种把所有逻辑判断放在一个if中完成,会使用一些与或非逻辑运算,如果逻辑判断条件过多,如果放在一个if判断中则会增加代码的可维护性,但第二种方法是一个条件一个条件判断,如果其中有一个不满足就退出,这样是根据if-else if顺序执行,来判断只有有不符合条件就退出、
4.2 核心代码
/*** @param paraYear* @return Is the given year leap? true or false;*/public static boolean isLeapYear(int paraYear) {if ((paraYear % 4 == 0) && (paraYear % 100 != 0) || (paraYear % 400 == 0)) {return true;} else {return false;}}/*** @param paraYear* @return Is the given year leap? Replace the complex condition with a number of if. return true or false*/public static boolean isLeapYearV2(int paraYear) {if (paraYear % 4 != 0) {return false;} else if (paraYear % 400 == 0) {return true;} else if (paraYear % 100 == 0) {return false;} else {return true;}}
day5 基本switch 语句
5.1 switch也属于条件分支语句
switch中表达式的值去和case后的值做匹配,若匹配正确则执行其后需要执行代码,遇到break结束执行。若没有case匹配,则最后就会执行default,default 分支不需要 break 语句
5.2 思考
(1)每一个case后都要跟break吗?
答案是否定的。不加break的话将会跳转到相应的case去执行且其以下的所有语句。
(2)switch和if条件语句有什么区别呢?
最明显差异是表示执行的结构,if中的表达式结果只能是boolean类型,而switch恰恰相反,他表示式结果可以是int,char等。我在实际使用过程中if语句用的比较多,但涉及到判断的if分支较多时,我会考率使用switch,这样效率会高一点
day6 基本for 语句
6.1 for语句中表达式的执行顺序
for(a;b;c)其中a,b,c为表达式,执行顺序:先执行a表达式,一般为初始化语句,再执行b表达式,一般式判断表达式,若为ture去执行循环体,执行完再执行c表达式,若不满足b表达式,则跳出循环。
6.2 代码
package basic;
public class ForStatement {/*** The entrance of the program.* @param args*/public static void main(String[] args) {forStatementTest();}/*** Method unit test.*/public static void forStatementTest(){int tempN = 0;System.out.println("1 add to " + tempN + " is: " + addToN(tempN));tempN = 0;System.out.println("1 add to " + tempN + " is: " + addToN(tempN));int tempStepLength = 1;tempN = 10;System.out.println("1 add to " + tempN + " with step length " + tempStepLength + " is: "+ addToNWithStepLength(tempN, tempStepLength));tempStepLength = 2;System.out.println("1 add to " + tempN + " with step length " + tempStepLength + " is: "+ addToNWithStepLength(tempN, tempStepLength));}/*** Add from 1 to N.* @param paraN The given upper bound.* @return The sum.*/public static int addToN(int paraN) {int resultSum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= paraN; i++) {resultSum += i;}return resultSum;}/*** Add from 1 to N with a step length.* @param paraN The given upper bound.* @param paraStepLength paraStepLength The given step length.* @return The sum.*/public static int addToNWithStepLength(int paraN, int paraStepLength) {int resultSum = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= paraN; i += paraStepLength) {resultSum += i;}return resultSum;}
}day7 矩阵元素相加
7.1 题目解读
矩阵用二维数组存储,计算二维数组的和,计算两个二维数组对应行列相加组成一个新的二维数组,都需要用到for循环遍历(行优先);对矩阵的赋值也需要循环遍历赋初值,在有循环时要避免死循环,确保循环是有限性的。
7.2 二维数组中
int[][] tempMatrix = new int[3][4];
tempMatrix.length; //代表行的长度
tempMatrix[0].length; //代表列的长度
代码:
package basic;import java.util.Arrays;
public class MatrixAddition {public static void main(String[] args) {matrixElementSumTest();matrixAdditionTest();}/*** Sum the elements of a matrix.* @param paraMatrix* @return The sum of all its elements.*/public static int matrixElementSum(int[][] paraMatrix) {int resultSum = 0;for (int i = 0; i < paraMatrix.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < paraMatrix[0].length; j++) {resultSum += paraMatrix[i][j];}}return resultSum;}/*** Unit test for respective method*/public static void matrixElementSumTest() {int[][] tempMatrix = new int[3][4];for (int i = 0; i < tempMatrix.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < tempMatrix[0].length; j++) {tempMatrix[i][j] = i * 10 + j;}}System.out.println("The matrix is: \r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempMatrix));System.out.println("The matrix element sum is: " + matrixElementSum(tempMatrix) + "\r\n");}/*** Add two matrices. Attention: NO error check is provided at this moment.* @param paraMatrix1 The first matrix.* @param paraMatrix2 The second matrix. It should have the same size as the first one's* @return The addition of these matrices.*/public static int[][] matrixAddition(int[][] paraMatrix1, int[][] paraMatrix2) {int[][] resultMatrix = new int[paraMatrix1.length][paraMatrix1[0].length];for (int i = 0; i < paraMatrix1.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < paraMatrix1[0].length; j++) {resultMatrix[i][j] = paraMatrix1[i][j] + paraMatrix2[i][j];}}return resultMatrix;}/*** Unit test for respective method.*/public static void matrixAdditionTest() {int[][] tempMatrix = new int[3][4];for (int i = 0; i < tempMatrix.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < tempMatrix[0].length; j++) {tempMatrix[i][j] = i * 10 + j;}}System.out.println("The matrix is: \r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempMatrix));int[][] tempNewMatrix = matrixAddition(tempMatrix, tempMatrix);System.out.println("The new matrix is: \r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempNewMatrix));}
}
day8 矩阵相乘
8.1 题目解读
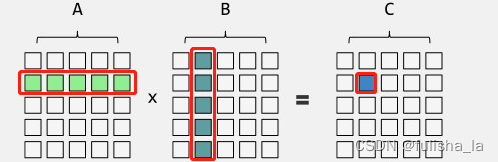
矩阵相乘(只有第一个矩阵的列和第二个矩阵的行相等): a矩阵(mn),b矩阵(np)则能相乘,且相乘后的矩阵为m*p。故在矩阵相乘是在一定条件下才能进行,需要用到if判断。
8.2代码
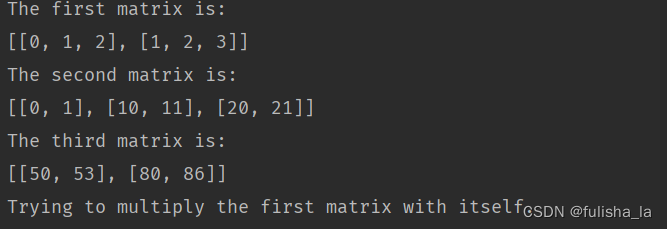
package basic;import java.util.Arrays;public class MatrixMultiplication {public static void main(String[] args) {matrixMultiplicationTest();}/*** Matrix multiplication. The columns of the first matrix should be equal to the rows of the second one.* @param paraFirstMatrix The first matrix.* @param paraSecondMatrix The second matrix* @return The result matrix.*/public static int[][] multiplication(int[][] paraFirstMatrix, int[][] paraSecondMatrix){//m*n n*p == m*pint m = paraFirstMatrix.length;int n = paraFirstMatrix[0].length;int p = paraSecondMatrix[0].length;// Step 1. Dimension check.if (paraSecondMatrix.length != n) {System.out.println("The two matrices cannot be multiplied.");return null;}// Step 2. The loop. m*n n*p == m*pint[][] resultMatrix = new int[m][p];for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < p; j++) {for (int k = 0; k < n; k++) {resultMatrix[i][j] += paraFirstMatrix[i][k] * paraSecondMatrix[k][j];}}}return resultMatrix;}public static void matrixMultiplicationTest(){int[][] tempFirstMatrix = new int[2][3];for (int i = 0; i < tempFirstMatrix.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < tempFirstMatrix[0].length; j++) {tempFirstMatrix[i][j] = i + j;}}System.out.println("The first matrix is: \r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempFirstMatrix));int[][] tempSecondMatrix = new int[3][2];for (int i = 0; i < tempSecondMatrix.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < tempSecondMatrix[0].length; j++) {tempSecondMatrix[i][j] = i * 10 + j;}}System.out.println("The second matrix is: \r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempSecondMatrix));int[][] tempThirdMatrix = multiplication(tempFirstMatrix, tempSecondMatrix);System.out.println("The third matrix is: \r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempThirdMatrix));System.out.println("Trying to multiply the first matrix with itself.\r\n");tempThirdMatrix = multiplication(tempFirstMatrix, tempFirstMatrix);System.out.println("The result matrix is: \r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(tempThirdMatrix));}
}
day9 while 语句
代码
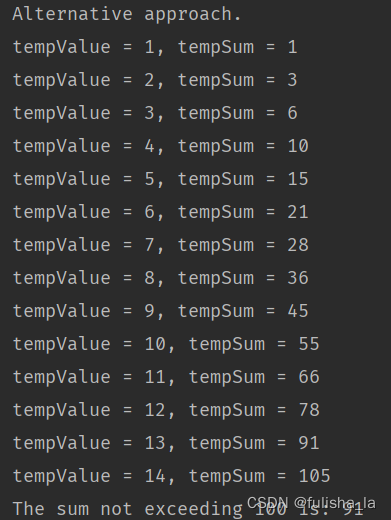
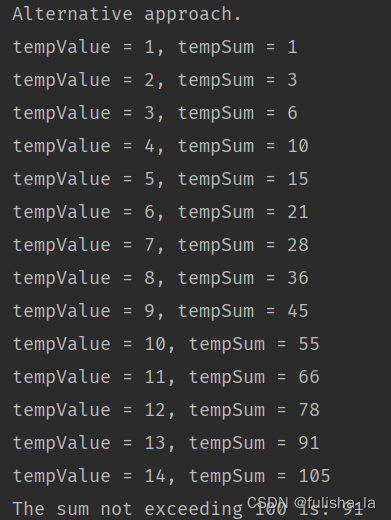
还有一种循环是 do…while,其循环至少要执行一次循环体,而for和while循环需要先判断条件是否成立 在决定是否执行循环语句
package basic;public class WhileStatement {public static void main(String[] args) {whileStatementTest();}/*** The sum not exceeding a given value.*/public static void whileStatementTest() {int tempMax = 100;int tempValue = 0;int tempSum = 0;// Approach 1.while (tempSum <= tempMax) {tempValue++;tempSum += tempValue;System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + ", tempSum = " + tempSum);}tempSum -= tempValue;System.out.println("The sum not exceeding " + tempMax + " is: " + tempSum);// Approach 2.System.out.println("\r\nAlternative approach.");tempValue = 0;tempSum = 0;while (true) {tempValue++;tempSum += tempValue;System.out.println("tempValue = " + tempValue + ", tempSum = " + tempSum);if (tempMax < tempSum) {break;}}tempSum -= tempValue;System.out.println("The sum not exceeding " + tempMax + " is: " + tempSum);}
}
day10 综合任务 1
10.1 题目解读
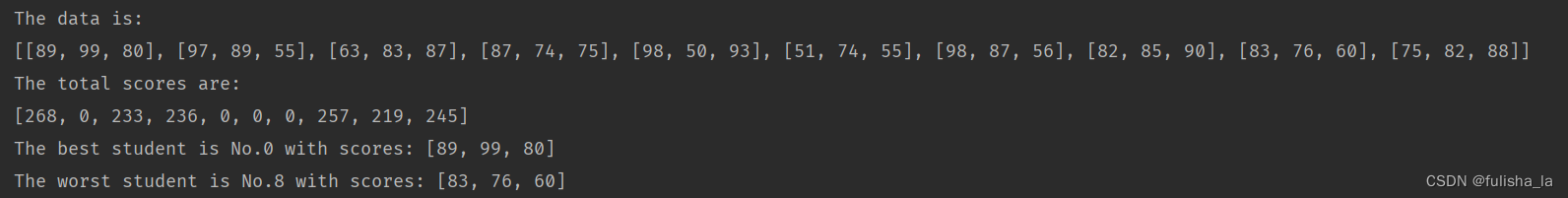
学生的成绩存放于一个矩阵,其中行表示学生,列表示科目。如:第 0 行表示第 0 个学生的数学、语文、英语成绩。要求:进行学生成绩的随机生成, 区间为 [50, 100];找出成绩最好、最差的同学。但有挂科的同学不参加评比.
- 1.初始化学生成绩(会涉及到随机生成数据的区间范围:Random)
- 2.通过for循环来计算学生总成绩并排除挂科同学(借助:break,continue关键字)
- 3.for循环+if判断来找出成绩最好和最差的学生
10.2 代码
package basic;import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class Task1 {public static void main(String[] args) {task1();}public static void task1(){//step1:Generate the data with n students and m courses.int n = 10;int m = 3;int lowerBound = 50;int upperBound = 100;int threshold = 60;// Here we have to use an object to generate random numbers.Random tempRandom = new Random();int[][] data = new int[n][m];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {data[i][j] = lowerBound + tempRandom.nextInt(upperBound - lowerBound);}}System.out.println("The data is:\r\n" + Arrays.deepToString(data));// Step 2. Compute the total score of each student.int[] totalScores = new int[n];for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {if (data[i][j] < threshold) {totalScores[i] = 0;break;}totalScores[i] += data[i][j];}}System.out.println("The total scores are:\r\n" + Arrays.toString(totalScores));// Step 3. Find the best and worst student.// Typical initialization for index: invalid value.int tempBestIndex = -1;int tempWorstIndex = -1;// Typical initialization for best and worst values.// They must be replaced by valid values.int tempBestScore = 0;int tempWorstScore = m * upperBound + 1;for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {// Do not consider failed students.if (totalScores[i] == 0) {continue;}if (tempBestScore < totalScores[i]) {tempBestScore = totalScores[i];tempBestIndex = i;}// Attention: This if statement cannot be combined with the last one using "else if", because a student can be both the best and the// worst. I found this bug while setting upperBound = 65.if (tempWorstScore > totalScores[i]) {tempWorstScore = totalScores[i];tempWorstIndex = i;}}// Step 4. Output the student number and score.if (tempBestIndex == -1) {System.out.println("Cannot find best student. All students have failed.");} else {System.out.println("The best student is No." + tempBestIndex + " with scores: "+ Arrays.toString(data[tempBestIndex]));}if (tempWorstIndex == -1) {System.out.println("Cannot find worst student. All students have failed.");} else {System.out.println("The worst student is No." + tempWorstIndex + " with scores: "+ Arrays.toString(data[tempWorstIndex]));}}
}
自我小结
三大结构
不管在c或者java,都会涉及到三大结构:顺序结构,选择结构,分支结构;通过对这三大结构的组合使用就可以解决一些很复杂的问题。
(1) 顺序结构:即按照代码的书写顺序依次执行,不存在跳转或者判断
- 要避免代码冗余,可以通过封装相应的方法或类来避免;例如day4中我们可以专门封装一个方法来判断是否为闰年,而避免每次都去重复写来判断
- 需要注意变量的使用范围等。例如day4中main方法中变量tempYear,正因为代码会顺序执行,所以可以对tempYear多次赋值从而覆盖前面的值。
(2)选择结构:会根据指定的判定条件去执行不同的代码块内容,如在day3,day4:if结构;if-else结构;if-else if结构;day5:switch结构
- 在选择结构中,要保证我们的判定条件是正确的
(3)循环结构:会根据指定的条件重复执行一段代码块内容,直到条件不符合跳出循环,如在day6-9中 for循环,while循环,除此之外还有do…while循环
- 循环条件要保证条件是能正确跳出循环条件的,否则会导致程序进入死循环
