网站建设能用手机制作吗竞价排名服务
对于排序算法,是我们在数据结构阶段,必须要牢牢掌握的一门知识体系,但是,对于排序算法,里面涉及到的思路,代码……各种时间复杂度等,都需要我们,记在脑袋瓜里面!!尽量一丢丢不要出现差错!面试所必备的精彩提问!!
言归正传:对于排序,我们首先需要知道的是:排序的概念!!
排序的概念!
所谓的排序,,就是使一串记录,按照其中的某个或者某些关键字的大小,递增递减的排序起来的操作!!
稳定性:假定在待排序的记录序列中,存在多个具有相同的关键字的记录,若经过排序,这些记录相对次序保持不变,即在原序列中,r[i]=r[j],且r[i]在r[j]之前,而在排序后的序列中,r[i]仍然在r[j]之前,这种排序算法是稳定的,否则是不稳定的!!
就比如:9 5 2 7 3 6 4 5 8 0 这些数据而言!

内部排序:数据元素部分放在内存的排序
外部排序:数据元素不能同时放在内存中,根据排序过程的要求不同,在内存与外存之间移动数据的排序(要排序的数据,在内存中放不下!!)
下面笔者就以七种常见的排序算法为列,来带大家走进排序!!(直接插入排序,希尔排序,选择排序,堆排序,冒泡排序,快速排序,归并排序)
1.插入排序:
插入排序:把待排序的记录按照其关键码值的大小,逐个插入到一个已经排序好的有序序列中,直到所有的记录插完为止,从而得到一个新的有序序列(扑克牌)
下面请看笔者的代码:
public static void insertSort(int[] arr){//对传入的数组进行排序for (int i = 1; i<arr.length; i++){for (int j = i-1; j>=0; j--){if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){//稳定的int temp = arr[j];arr[j] = arr[j+1];arr[j+1] = temp;}elsebreak;}}System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array={12,56,32,67,10,19,4};insertSort(array);}2.希尔排序
希尔排序的思想:先选定一个整数,把待排序文件中的所有记录分成多个组,所有距离为一样的放在同一个组内,并对每一组的记录进行插入排序,取重复上述分组和排序的工作,当达到=1时,所有记录在统一组内排序好(先分组,5组,3组,最后为1组)
假设初始的数据为: 9 1 2 5 7 4 8 6 3 5
那么,我们有着一下 的简单排序过程:
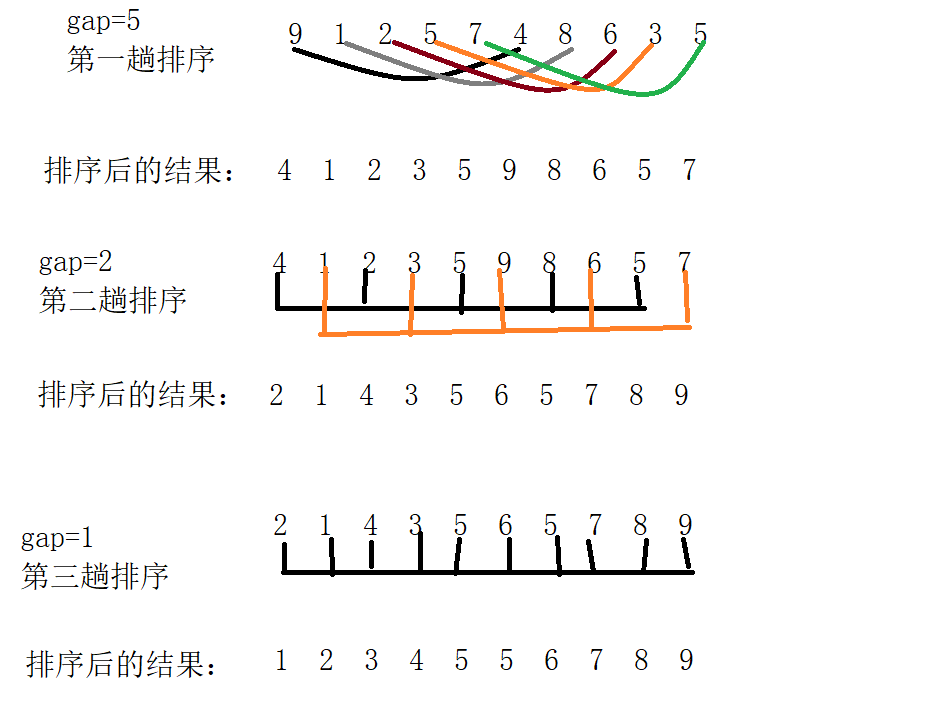
经过上述的过程,我们可以看出:组数越多,每组进行排序的数据越少!(两两交换(使用插入排序)越有序越快),组数越少,每组数据越多(数据在慢慢变得有序)
那么,我们对于希尔排序,有着一下的几点总结:
希尔排序是对直接插入排序算法的优化!
当gap>1时,都是预排序,目的是让数组接近有序,当gap=1时,数组已经接近有序了,这样就会很快,这样整体而言,可以达到优化的效果,我们实现后可以进行性能测试的对比!
希尔排序的时间复杂度不好计算,因为gap的取值方法很多,导致很难去计算,因此在好些书中,给出的希尔排序的时间复杂度不固定!
有了上述的思考,我们接下来就该实现一下代码了:
public static void shellSort(int[] array){int gap=array.length;//分组while (gap>1){shell(array,gap);gap=gap/2;}//整体进行插入排序,此时gap=1shell(array,1);}//插入排序public static void shell(int[] array,int gap){for (int i = 0; i <array.length; i++) {int tmp=array[i];int j=i-gap;for(;j>=0;j=j-gap){if (array[j]>tmp){array[j+gap]=array[j];}else {break;}}array[j+gap]=tmp;}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array={12,56,32,67,10,19,4};shellSort(array);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}3.选择排序
在了解选择排序之前,我们需要知道的是:
选择排序的思想:每一次从待排序的数据元素中选出最小(最大)的一个元素,存放在序列的起始位置,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完,直接选择排序!
第一次从R[0]到R[n-1]中选出最小值,与R[0]进行交换,第二次从R[1]到R[n-1]中选出最小值与R[1]交换……,以此类推,从而得到从小到大的有序排序
经过上面的简单分析,我们可以得出下列的有效代码:
public static void selectSort(int[] array) {for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {int minIndex = i;for (int j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {if (array[j] < array[minIndex]) {minIndex = j;//minIndex保存最小数据的下标值!}}swap(array, i, minIndex);}}private static void swap(int[] array,int i,int j){int tmp=array[i];array[i]=array[j];array[j]=tmp;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array={12,56,32,67,10,4};selectSort(array);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}4.堆排序
对于堆排序,是指利用堆积树(堆),这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法,它是一种选择排序,通过堆来进行选择数据
需要注意的是:排升序建大堆,排降序建小堆!!
那么,根据笔者之前的堆排序的环节:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_64308540/article/details/129217324?spm=1001.2014.3001.5502我们可以有着一下的简单代码:
public static void heapSort(int[] array){createBigHeap(array);//创建一个大根堆int end=array.length-1;while (end>0){//等于0的时候就不换了swap(array,0,end);//交换shiftDown(array,0,end);//向下调整end--;}}private static void createBigHeap(int[] array){//建立大根堆从最后一颗子树开始for (int parent = (array.length-1-1)/2; parent >=0 ; parent--) {shiftDown(array,parent,array.length);//array,length是指结束位置}}//向下调整private static void shiftDown(int[] array,int parent,int len){int child=2*parent+1;while (child<len){//至少有左孩子if (child+1<len && array[child]<array[child+1]){//有右孩子//此时child是左孩子最大值的下标child++;}if (array[child]>array[parent]){swap(array,child,parent);//交换parent=child;child=2*parent+1;}else {break;}}}private static void swap(int[] array,int i,int j){int tmp=array[i];array[i]=array[j];array[j]=tmp;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array={12,56,32,67,10,4};heapSort(array);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}5.交换排序
对于交换排序,我们在之前就已经有过接触,其实就是最简单的冒泡排序
交换排序的基本思想:所谓交换就是根据序列中的两个记录键值的比较结果,交换这两个记录在序列中的位置!
交换排序的特点:将键值较大的记录向序列的尾部移动,键值较小的记录向序列的前部移动
下面笔者就以冒泡排序来进行书写代码:
方法1:
public static void bubblesort2(int[] array ) {//趟数for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {//每趟执行的次数boolean flg=false;for(int j=0;j<array.length-1-i;j++) {if(array[j]>array[j+1]) {int tmp=array[j+1];array[j+1]=array[j];array[j]=tmp;}flg=true;}if(flg==false) {return ;}}}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array={1,29,10,36,5,21,46,3,6};bubblesort2(array);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}方法2:
public static void bubbleSort2(int[] array){for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {for (int j = 0; j < array.length-1-i; j++) {if (array[j]>array[j+1])swap(array,j,j+1);}}}private static void swap(int[] array,int i,int j){int tmp=array[i];array[i]=array[j];array[j]=tmp;}public static void main(String[] args) {int[] array={12,56,32,67,10,19,4};bubbleSort2(array);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));}在上述代码中,方法1是对方法2的简单优化!!
在方法1中,我们通过一个:boolean flg=false;来优化了代码!!原因在于,在进行冒泡排序的时候,可能对于一串数据,排到一半就有序了,那么,在没有优化之前,肯定还得一个一个尝试去遍历,但是,在优化以后,可以节约时间!!
6.快速排序
快速排序的思想:任取待排序元素序列中的某元素(一般是第一个元素),作为基准值,按照该排序码,将待排序的集合分为两个子序列,左子序中的所有元素均小于基准值,右子序中的所有元素均大于基准值,然后最左右子序列都重复该过程,直到所有的元素都排序在相应的位置为止!!
对于上述的简单思想,我们有着挖坑法!Hoare法!
下面我们先讲解一下挖坑法:
先将第一个数据存放在一个临时变量key中,形成一个坑位!
设置两个变量i,j,排序开始的时候,i=0,j=N-1!
以第一个数组元素作为关键数据,赋值给key,即key=A[0]!
从j开始向前搜素,即由后开始向前搜素(j--),找到第一个小于key的值A[j],将A[j]与A[i]的值进行交换!
从i开始向后搜素,即由前开始向后搜素(i++),找到第一个大于key的值A[i],将A[i]与A[j]的值交换!
重复步骤3,4,直到i==j为止!
对于上述的思路,我们可以用递归来实现!!
package zyh.example.demo.algorithm.kuaisupaixu;import java.util.Arrays;/**
* @ClassName KuaiPai13
* @Author zhangyonghui
* @Description
* @Date 2022/3/29 11:26
* @Version 1.0
**/
public class KuaiPai13 {public static void main(String[] args) {int[] arr = new int[]{4, 7, 6, 5, 3, 2, 8, 1};quickSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));}/*** 快速排序--挖坑法* @param arr 数组* @param startIndex 左边界索引* @param endIndex 右边界索引*/public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int startIndex, int endIndex) {// 递归结束条件:startIndex大等于endIndex的时候if (startIndex >= endIndex) {return;}// 得到基准元素位置int pivotIndex = partition(arr, startIndex, endIndex);// 用分治法递归数列的两部分quickSort(arr, startIndex, pivotIndex - 1);quickSort(arr, pivotIndex + 1, endIndex);}/*** 具体每一轮的快速排序:* @param arr 数组* @param startIndex 左边界索引* @param endIndex 右边界索引* @return 返回基准值的位置,此时基准值左边的元素都小于基准值,基准值右边的元素都大于基准值*/private static int partition(int[] arr, int startIndex, int endIndex) {// 取第一个位置的元素作为基准元素int pivot = arr[startIndex];// 初始化坑的位置,初始等于pivot基准值的位置int kengIndex = startIndex;//初始化左右游标/指针int leftYb = startIndex;int rightYb = endIndex;//大循环在左右指针重合时结束while ( leftYb<rightYb ) {//right指针从右向左进行比较// leftYb<rightYb ,左游标永远小于右游标,是遍历元素并发生元素变动的前提:while ( leftYb<rightYb) {// 先遍历右边,// 如果元素大于基准值--右游标左移:if (arr[rightYb] >= pivot) {rightYb--;}else{ //如果右边的当前元素小于基准值了,那么将该元素填入坑中,该元素本来的位置成为新的坑;arr[kengIndex] = arr[rightYb];kengIndex = rightYb;leftYb++;break;}}//再遍历左边,// leftYb<rightYb ,左游标永远小于右游标,是遍历元素并发生元素变动的前提:while (leftYb<rightYb) {//如果元素小于基准值--左游标右移,if (arr[leftYb] <= pivot) {leftYb++;}else{ //如果左边的当前元素大于基准值了,那么将该元素填入坑中,该元素本来的位置成为新的坑;arr[kengIndex] = arr[leftYb];kengIndex = leftYb;rightYb--;break;}}}//跳出了大循环,说明此时此刻左右游标是重合的,这时将基准值放在重合位置(最后一个坑),// 此时,基准值左边的元素都小于基准值,基准值右边的元素都大于基准值,这一轮交换宣告结束;arr[kengIndex] = pivot;return kengIndex;}}接下来进入Hoare法!
right找到比基准小的停下来,left找到比基准大的停下来,进行比较,循环往复,最后当right==left的时候,将此时对应的值与基准进行比较!
请看笔者代码:
public class Main {static int[] a= {5, 3, 1, 9, 8, 2, 4, 7};public static void main(String[] args) {fastsort(0, a.length-1);for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {System.out.print(a[i] + " ");}}private static int Hoare(int l, int r) {int p = a[l];int i = l-1;int j = r+1 ;while (true) {do {j--;} while (a[j] > p);do {i++;} while (a[i] < p);if (i < j) {int temp = a[i];a[i] = a[j];a[j] = temp;} elsereturn j;}}private static void fastsort(int l, int r) {if (l < r) {int s = Hoare(l, r);fastsort(l, s);fastsort(s+1, r);}}
}7.归并排序
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法的一个非常典型的应用,将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列,即,先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列断间有序!
主要的思路及其过程,如下图所示:
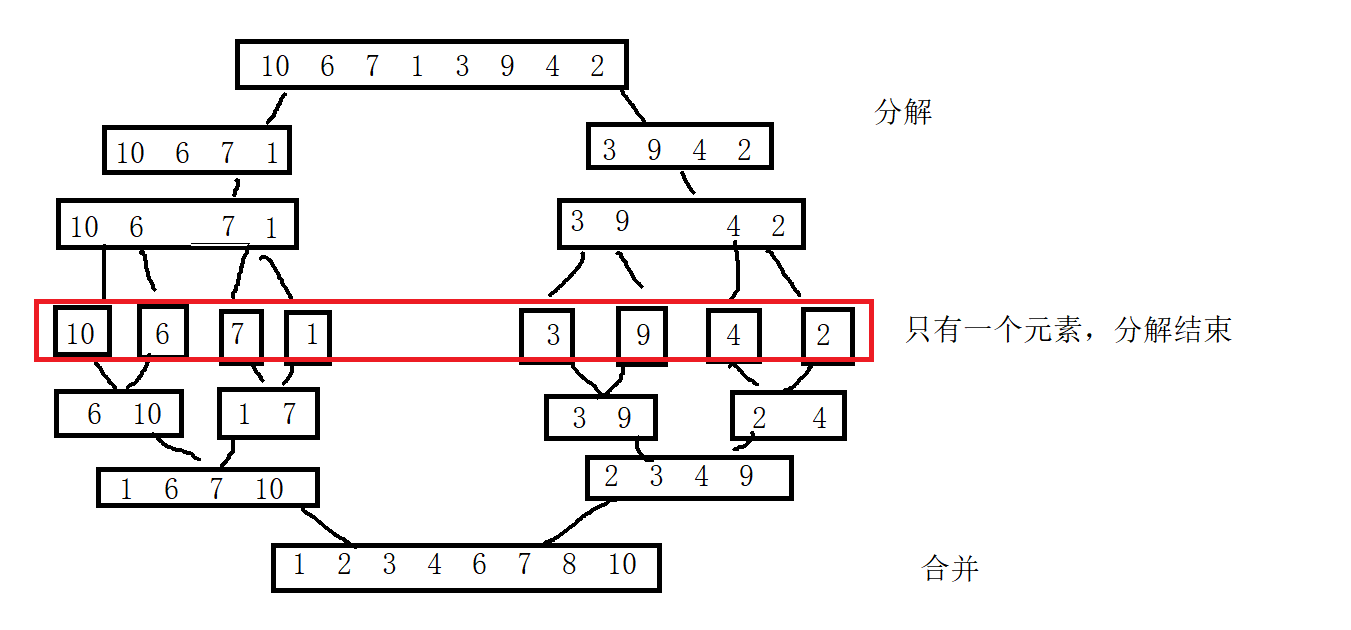
那么,接下来请看代码吧!!(递归实现)
//递归实现
public static void mergeSort(int[] array){mergeSortFunc(array,0, array.length);}private static void mergeSortFunc(int[] array,int left,int right){if (left>=right){return;}//分解int mid=(left+right)/2;mergeSortFunc(array,left,mid);mergeSortFunc(array,mid+1,right);merge(array,left,right,mid);//合并}private static void merge(int[] array,int start,int end,int mid){int s1=start;int s2=mid+1;int[] tmp=new int[end-start+1];//申请一个数组int k=0;//tmp数组下标while (s1<=mid && s2<=end){if (array[s1]<= array[s2]){tmp[k++]=array[s1++];}else {tmp[k++]=array[s2++];}}while (s1<=mid){tmp[k++]=array[s1++];}while (s2<=end){tmp[k++]=array[s2++];}for (int i = 0; i < tmp.length; i++) {array[i+start]=tmp[i];}}感兴趣的老铁,可以看一下非递归实现的:
//非递归public static void mergeSort2(int[] array){int gap=1;while (gap<array.length){for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {int left=i;int mid=left+gap+1;if (mid>= array.length){mid=array.length-1;}int right=mid+gap;if (right>=array.length){right=array.length-1;}merge(array,left,right,mid);}gap=gap*2;}}七大排序算法大致就到此结束了!!拜拜!
