俄华网站建设成人职业培训学校
前言
当前ChatGPT非常火爆,对于程序员来说,ChatGPT可以帮助编写很多有用的代码。比如:在算法的实现上,就可以替我们省很多事。所以,小试牛刀一下,看看ChatGPT生成了排序算法怎么样?
简介
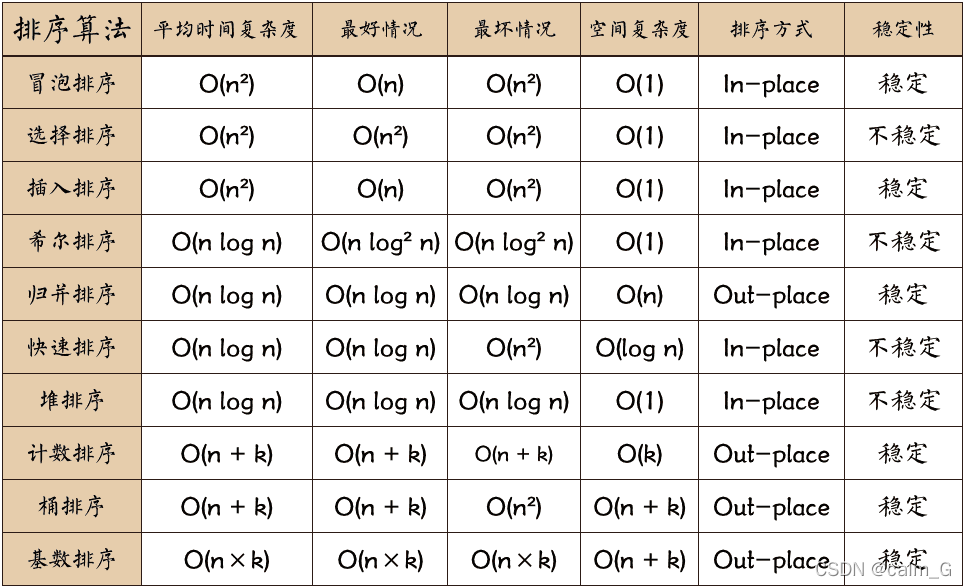
排序算法可以分为内部排序和外部排序,内部排序是数据记录在内存中进行排序,而外部排序是因排序的数据很大,一次不能容纳全部的排序记录,在排序过程中需要访问外存。常见的内部排序算法有:插入排序、希尔排序、选择排序、冒泡排序、归并排序、快速排序、堆排序、基数排序等。用一张图概括:
image
1. 冒泡排序
冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)也是一种简单直观的排序算法。假设长度为n的数组arr,要按照从小到大排序。则冒泡排序的具体过程可以描述为:首先从数组的第一个元素开始到数组最后一个元素为止,对数组中相邻的两个元素进行比较,如果位于数组左端的元素大于数组右端的元素,则交换这两个元素在数组中的位置。这样操作后数组最右端的元素即为该数组中所有元素的最大值。接着对该数组除最右端的n-1个元素进行同样的操作,再接着对剩下的n-2个元素做同样的操作,直到整个数组有序排列。
// Bubble sort algorithm implementation in Go
// 生成冒泡排序
func bubbleSort(arr []int) {n := len(arr)for i := 0; i < n-1; i++ {for j := 0; j < n-i-1; j++ {if arr[j] > arr[j+1] {arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]}}}
} // Example usage:
// arr := []int{64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90}
// bubbleSort(arr)
// fmt.Println("Sorted array:", arr)2. 选择排序
选择排序是一种简单直观的排序算法,无论什么数据进去都是 O(n²) 的时间复杂度。所以用到它的时候,数据规模越小越好。唯一的好处可能就是不占用额外的内存空间了吧。具体来说,假设长度为n的数组arr,要按照从小到大排序,那么先从n个数字中找到最小值min1,如果最小值min1的位置不在数组的最左端(也就是min1不等于arr0),则将最小值min1和arr0交换,接着在剩下的n-1个数字中找到最小值min2,如果最小值min2不等于arr1,则交换这两个数字,依次类推,直到数组arr有序排列。算法的时间复杂度为O(n^2)。
// Selection sort implementation in Go
func selectionSort(arr []int) {n := len(arr)for i := 0; i < n-1; i++ {minIndex := ifor j := i + 1; j < n; j++ {if arr[j] < arr[minIndex] {minIndex = j}}arr[i], arr[minIndex] = arr[minIndex], arr[i]}
}// Example usage
func main() {arr := []int{64, 25, 12, 22, 11}selectionSort(arr)fmt.Println("Sorted array:", arr)
}3. 快速排序
快速排序通常明显比其他 Ο(nlogn) 算法更快,因为它的内部循环(inner loop)可以在大部分的架构上很有效率地被实现出来。快速排序的基本思想是:通过一趟排序将待排记录分割成独立的两部分,其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分记录的关键字小,则可分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,已达到整个序列有序。一趟快速排序的具体过程可描述为:从待排序列中任意选取一个记录(通常选取第一个记录)作为基准值,然后将记录中关键字比它小的记录都安置在它的位置之前,将记录中关键字比它大的记录都安置在它的位置之后。这样,以该基准值为分界线,将待排序列分成的两个子序列。它是处理大数据最快的排序算法之一了。该算法时间复杂度为O(n log n)。
// Here is an implementation of the quicksort algorithm in Go:func quicksort(arr []int) []int {if len(arr) < 2 {return arr}pivot := arr[0]var less []intvar greater []intfor _, num := range arr[1:] {if num <= pivot {less = append(less, num)} else {greater = append(greater, num)}}sorted := append(quicksort(less), pivot)sorted = append(sorted, quicksort(greater)...)return sorted
}// To use this function, simply pass in an unsorted slice of integers:
// sorted := quicksort([]int{3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9, 2, 6, 5, 3, 5})
// fmt.Println(sorted) // Output: [1 1 2 3 3 4 5 5 5 6 9]4. 插入排序
插入排序(Insertion-Sort)的算法描述是一种简单直观的排序算法。它的工作原理是通过构建有序序列,对于未排序数据,在已排序序列中从后向前扫描,找到相应位置并插入。例如要将数组arr=4,2,8,0,5,1排序,可以将4看做是一个有序序列,将2,8,0,5,1看做一个无序序列。无序序列中2比4小,于是将2插入到4的左边,此时有序序列变成了2,4,无序序列变成了8,0,5,1。无序序列中8比4大,于是将8插入到4的右边,有序序列变成了2,4,8,无序序列变成了0,5,1。以此类推,最终数组按照从小到大排序。该算法的时间复杂度为O(n^2)。
// Insertion sort implementation in Go
func insertionSort(arr []int) {for i := 1; i < len(arr); i++ {key := arr[i]j := i - 1for j >= 0 && arr[j] > key {arr[j+1] = arr[j]j = j - 1}arr[j+1] = key}
}// Call the insertion sort function with an example array
func main() {arr := []int{12, 11, 13, 5, 6}insertionSort(arr)fmt.Println("Sorted array:", arr)
}5. 希尔排序
希尔排序(Shell’s Sort)在插入排序算法的基础上进行了改进,算法的时间复杂度与前面几种算法相比有较大的改进,但希尔排序是非稳定排序算法。其算法的基本思想是:先将待排记录序列分割成为若干子序列分别进行插入排序,待整个序列中的记录"基本有序"时,再对全体记录进行一次直接插入排序。该算法时间复杂度为O(n log n)。
// ShellSort implements the Shell sort algorithm
func ShellSort(arr []int) {n := len(arr)gap := n / 2for gap > 0 {for i := gap; i < n; i++ {temp := arr[i]j := ifor j >= gap && arr[j-gap] > temp {arr[j] = arr[j-gap]j -= gap}arr[j] = temp}gap /= 2}
} // The above code implements the Shell sort algorithm in Go.6. 归并排序
归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法。该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。代价是需要额外的内存空间。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为2-路归并。 该算法时间复杂度为O(n log n)。
// Here is an implementation of 归并排序 (merge sort) in Go:func mergeSort(arr []int) []int {if len(arr) <= 1 {return arr}mid := len(arr) / 2left := mergeSort(arr[:mid])right := mergeSort(arr[mid:])return merge(left, right)
}func merge(left, right []int) []int {result := make([]int, 0)for len(left) > 0 || len(right) > 0 {if len(left) == 0 {return append(result, right...)}if len(right) == 0 {return append(result, left...)}if left[0] <= right[0] {result = append(result, left[0])left = left[1:]} else {result = append(result, right[0])right = right[1:]}}return result
}// To use this implementation, simply call mergeSort() with an array of integers as an argument. The function will return a sorted array.7. 堆排序
堆排序(Heapsort)是指利用堆这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法。堆积是一个近似完全二叉树的结构,并同时满足堆积的性质:即子结点的键值或索引总是小于(或者大于)它的父节点。堆排序可以说是一种利用堆的概念来排序的选择排序。分为两种方法:每个结点的值都大于等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为大顶堆;或者每个结点的值都小于等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为小顶堆。该算法时间复杂度为O(n log n)。
// HeapSort function implements the heap sort algorithm
func HeapSort(arr []int) {n := len(arr)// Build heap (rearrange array)for i := n/2 - 1; i >= 0; i-- {heapify(arr, n, i)}// One by one extract an element from heapfor i := n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {// Move current root to endarr[0], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[0]// call max heapify on the reduced heapheapify(arr, i, 0)}
}// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i which is
// an index in arr[]. n is size of heap
func heapify(arr []int, n, i int) {largest := i // Initialize largest as rootl := 2*i + 1 // left = 2*i + 1r := 2*i + 2 // right = 2*i + 2// If left child is larger than rootif l < n && arr[l] > arr[largest] {largest = l}// If right child is larger than largest so farif r < n && arr[r] > arr[largest] {largest = r}// If largest is not rootif largest != i {arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i]// Recursively heapify the affected sub-treeheapify(arr, n, largest)}
} // Example usage:
// arr := []int{12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7}
// HeapSort(arr)
// fmt.Println(arr) // Output: [5 6 7 11 12 13]8. 计数排序
计数排序的核心在于将输入的数据值转化为键存储在额外开辟的数组空间中。计数排序不是基于比较的排序算法。而是 作为一种线性时间复杂度的排序,计数排序要求输入的数据必须是有确定范围的整数。当输入的元素是 n 个 0 到 k 之间的整数时,它的运行时间是 Θ(n + k)。计数排序不是比较排序,排序的速度快于任何比较排序算法。由于用来计数的数组C的长度取决于待排序数组中数据的范围(等于待排序数组的最大值与最小值的差加上1),这使得计数排序对于数据范围很大的数组,需要大量时间和内存。该算法时间复杂度为O(n+k)。
// Counting sort implementation in Go
// 计数排序实现func countingSort(arr []int) []int {size := len(arr)if size == 0 {return arr}// Find the maximum element in the arraymax := arr[0]for i := 1; i < size; i++ {if arr[i] > max {max = arr[i]}}// Create a count array to store count of individual elements and initialize count array as 0count := make([]int, max+1)for i := 0; i < max+1; i++ {count[i] = 0}// Store count of each elementfor i := 0; i < size; i++ {count[arr[i]]++}// Store cumulative count of each elementfor i := 1; i < max+1; i++ {count[i] += count[i-1]}// Create the output arrayoutput := make([]int, size)for i := size - 1; i >= 0; i-- {output[count[arr[i]]-1] = arr[i]count[arr[i]]--}// Copy the output array to arr, so that arr now contains sorted elementsfor i := 0; i < size; i++ {arr[i] = output[i]}return arr
}9. 桶排序
桶排序是计数排序的升级版。它利用了函数的映射关系,高效与否的关键就在于这个映射函数的确定。桶排序 (Bucket sort)的工作的原理:假设输入数据服从均匀分布,将数据分到有限数量的桶里,每个桶再分别排序(有可能再使用别的排序算法或是以递归方式继续使用桶排序进行排)。为了使桶排序更加高效,我们需要做到这两点:在额外空间充足的情况下,尽量增大桶的数量;使用的映射函数能够将输入的 N 个数据均匀的分配到 K 个桶中。该算法时间复杂度为O(n+k)。
// Bucket sort implementation in Go
// 桶排序实现func bucketSort(arr []float64) []float64 {// Create bucketsnum := len(arr)buckets := make([][]float64, num)// Add values to bucketsfor i := 0; i < num; i++ {bucketIndex := int(arr[i] * float64(num))buckets[bucketIndex] = append(buckets[bucketIndex], arr[i])}// Sort buckets and place back into input arrayk := 0for i := 0; i < num; i++ {sort.Float64s(buckets[i])for _, val := range buckets[i] {arr[k] = valk++}}return arr
}10. 基数排序
基数排序是一种非比较型整数排序算法,其原理是将整数按位数切割成不同的数字,然后按每个位数分别比较。由于整数也可以表达字符串(比如名字或日期)和特定格式的浮点数,所以基数排序也不是只能使用于整数。基数排序是按照低位先排序,然后收集;再按照高位排序,然后再收集;依次类推,直到最高位。有时候有些属性是有优先级顺序的,先按低优先级排序,再按高优先级排序。最后的次序就是高优先级高的在前,高优先级相同的低优先级高的在前。该算法时间复杂度为O(n+k)。
// Radix sort implementation in Go
func radixSort(arr []int) {// Find the maximum number to know number of digitsmax := arr[0]for i := 1; i < len(arr); i++ {if arr[i] > max {max = arr[i]}}// Do counting sort for every digit. Note that instead// of passing digit number, exp is passed. exp is 10^i// where i is current digit numberfor exp := 1; max/exp > 0; exp *= 10 {countingSort(arr, exp)}
}// A utility function to do counting sort of arr[] according to
// the digit represented by exp.
func countingSort(arr []int, exp int) {n := len(arr)// The output array elements that will have sorted arroutput := make([]int, n)// Initialize count array as 0count := make([]int, 10)// Store count of occurrences in count[]for i := 0; i < n; i++ {index := (arr[i] / exp) % 10count[index]++}// Change count[i] so that count[i] now contains actual// position of this digit in output[]for i := 1; i < 10; i++ {count[i] += count[i-1]}// Build the output arrayfor i := n - 1; i >= 0; i-- {index := (arr[i] / exp) % 10output[count[index]-1] = arr[i]count[index]--}// Copy the output array to arr[], so that arr[] now// contains sorted numbers according to current digitfor i := 0; i < n; i++ {arr[i] = output[i]}
}
